| Code | Types | Material | Diameter | EFL | Coating | Unit Price | Delivery | Cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1105-003 | Ball | Sapphire | 1.0mm | 0.57mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-003 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 1.0mm | - | None | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1105-006 | Ball | Sapphire | 2.0mm | 1.15mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-006 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 2.0mm | - | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1105-009 | Ball | Sapphire | 3.0mm | 1.72mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-009 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 3.0mm | - | None | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1105-012 | Ball | Sapphire | 4.0mm | 2.30mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-012 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 4.0mm | - | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1105-015 | Ball | Sapphire | 5.0mm | 2.87mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-015 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 5.0mm | - | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1105-018 | Ball | Sapphire | 6.0mm | 3.45mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-018 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 6.0mm | - | None | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1105-021 | Ball | Sapphire | 7.0mm | 4.02mm | None | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1106-021 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 7.0mm | - | None | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1105-024 | Ball | Sapphire | 8.0mm | 4.60mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-024 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 8.0mm | - | None | Inquiry | Inquiry | |
| 1105-027 | Ball | Sapphire | 9.0mm | 5.17mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-027 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 9.0mm | - | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1105-030 | Ball | Sapphire | 10.0mm | 5.75mm | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days | |
| 1106-030 | Half-Ball | Sapphire | 10.0mm | - | None | Inquire | 2~3 Days |
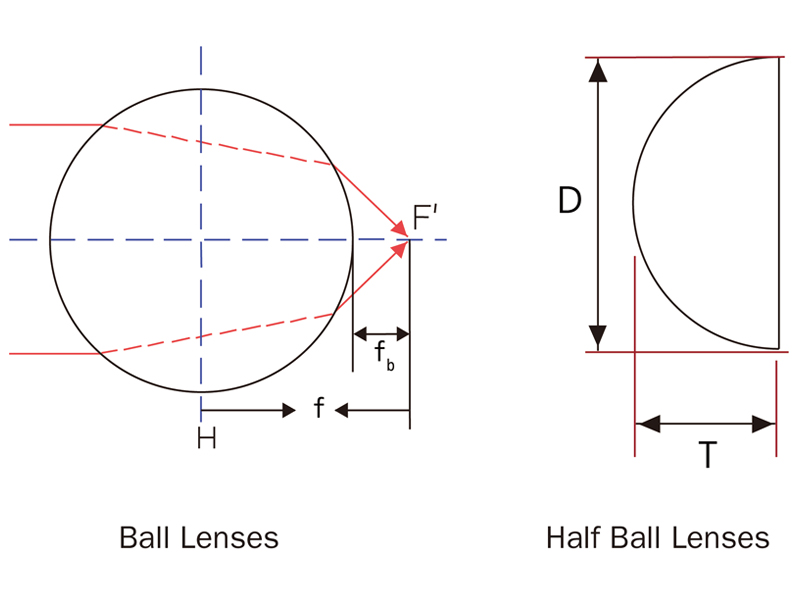
What are Ball lenses and Half-ball lenses:
Ball lenses belong to a special form of biconvex lenses which have the geometry of a ball (sphere). Ball lenses are manufactured from a single optical material with good transmittance in the wavelength region of interest. The conventional applications of ball lenses include focusing light in the field of fibers (e.g. laser to fiber coupling, fiber to fiber coupling), emitters, and detectors, in major to collimate light depending on the geometries of the input light source. Also, ball lenses could be ball pre-forms of aspheric lenses where ball lenses are deformed on purpose to prevent spherical aberrations.
Half-Ball lenses are variants of ball lenses, obtained through cutting the ball lenses in half. Due to the ease of mounting derived from the one flat surface, half-ball lenses are more convenient for applications where space limitations exist and more compact designs are required, such as fiber communication, endoscopes, microscopes, optical pick-up devices, and laser measurement facilities.
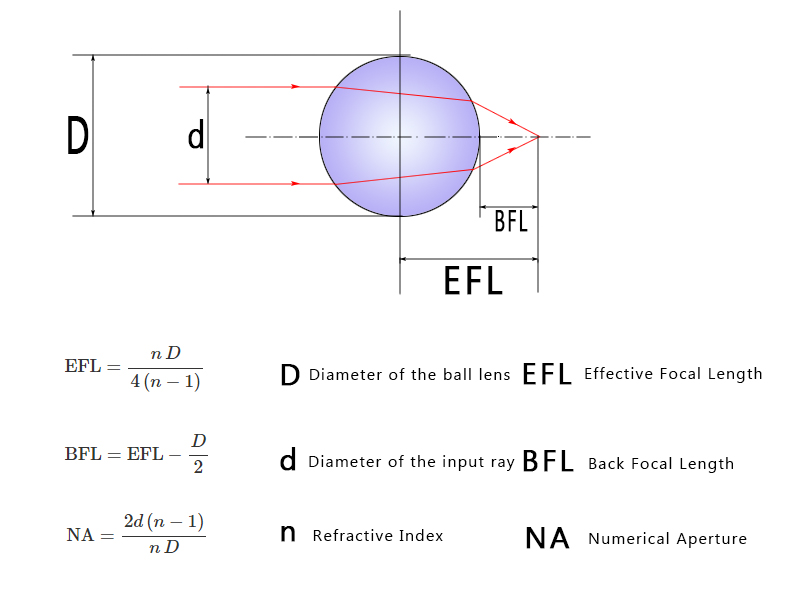
There are three essential parameters of ball lenses and half-ball lenses. One is the effective focal length (EFL), which is the distance between a plane through the center of the lens and the beam waist (focus) of a collimated input beam. Another is back focal length (BFL), defined as the distance of the focal point from the lens surface, therefore half the diameter smaller than the EFL. The last is numerical aperture (NA), for collimated incident light, the numerical aperture (NA) of the ball lens is dependent on the size of the ball lens (D), its index of refraction (n), and the diameter of the input source (d). Numerical aperture is proportionate to the resolution of the lens, the larger the NA, the more the light is collected by the lens.
The calculation equations of the EFL, BFL, and NA and shown in the figure below:
Here are some important features of Sapphire:
Sapphire:
Optical-grade Sapphires chosen to produce optical components are Alpha Single Crystal Sapphires, chemical formula Al2O3, with a wide transmission range from 0.225-5.5μm. Sapphire has a hexagonal structure. The lattice constant is a=b=4.758A, c=12.991A, and the refractive index is 1.762-1.770. Its strong covalent bonds contribute to the enduring and solid nature of sapphire. Its Mohs hardness is 9, ranking right after diamond, and its anti-compression strength is between 1.9-24 GPa. Young’s Modulus of sapphire is 380Gpa, which is about twice the magnitude of irons. The melting temperature of sapphire is high,2045 °C, which enables sapphire to be engaged in manifolds of applications requiring high thermal loads.
Sapphire Ball lenses and Half Ball lenses are ideal for demanding applications in the IR spectrum because of wide transmission range of 0.15-5.5μm, superior surface hardness (9 on the Mohs scale, the third hardest mineral, after diamond at 10 and moissanite at 9.5, which means high resistance to scratch and abrasion), high thermal conductivities, outstanding dielectric properties and resistance to common chemical acids and alkalis. In addition, sapphire features a high refractive index, which is advantageous for light collection. North Optics offers off-the-shelf and custom Sapphire Ball Lenses and Half Ball Lenses with a maximum diameter of 300mm, AR coatings are available.
Specifications:
| Materials | Optical grade sapphire crystals | Diameter Range | ~300mm |
| Diameter Tolerance | +0.0/-0.2mm | Thickness Tolerance | +/-0.2mm |
| Surface Quality | 60/40 S/D | Fringes (N) | 3 |
| Irregularity (delta N) | 1 | Centration | 3' |
| Chamfer | 0.1-0.3mmx45 degree |
Physical and Optical Properties:
| Transmission Range | 0.17 to 5.5 μm | Refractive Index | No 1.75449; Ne 1.74663 at 1.06 μm (1) |
| Reflection Loss | 14% at 1.06 μm | Absorption Coefficient | 0.3 x 10-3 cm-1 at 2.4 μm(2) |
| Reststrahlen Peak | 13.5 μm | dn/dT | 13.1 x 10-6 at 0.546 μm(3) |
| dn/dμ = 0 | 1.5 μm | Density | 3.97 g/cc |
| Melting Point | 2040°C | Thermal Conductivity | 27.21 W m-1 K-1 at 300K |
| Thermal Expansion | 5.6 (para) & 5.0 (perp)x 10-6/K* | Hardness | Knoop 2000 with 2000gindenter |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 763 J Kg-1 K-1 at 293K(4) | Dielectric Constant | 11.5 (para) 9.4 (perp) 、at 1MHz |
| Youngs Modulus (E) | 335 GPa | Shear Modulus (G) | 148.1 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus (K) | 240 GPa | Elastic Coefficients | C11=496 C12=164 C13=115 C33=498 C44=148 |
| Apparent Elastic Limit | 300 MPa (45,000 psi) | Poisson Ratio | 0.25 |
| Solubility | 98 x 10-6 g/100g water | Molecular Weight | 101.96 |
| Class/Structure | Trigonal (hex), R3c |

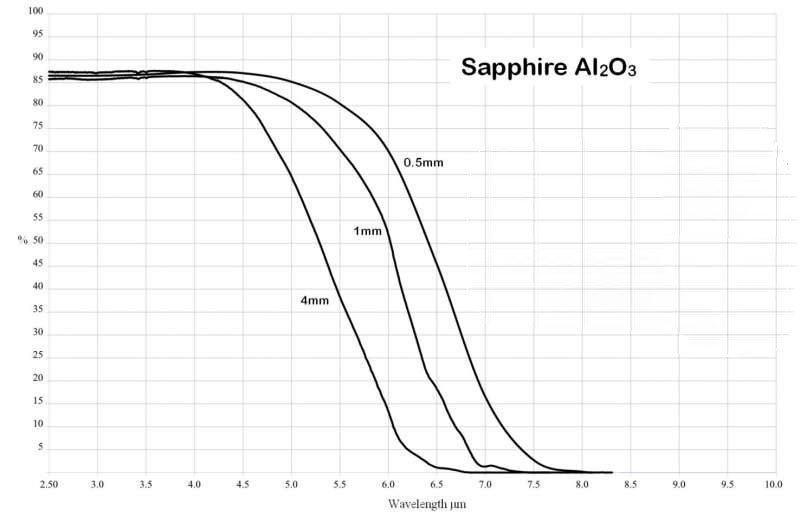
Curves:
1. Transmission of Sapphire at Infrared wavelength range (no coating)
2. Transmission of Sapphire at UV wavelength range ( no coating)
