Specifications of BBO Pockels cells
| Aperture | TBA | Quarter-wave voltage | 3.4KV |
| Optical Transmission | >98% | Damage Threshold | 500MW/cm2 @ 10ns, 1064nm |
| Wavefront Distortion @ 1064 | < Lambda/8 | Typical Capacitance | < 3pF |
| Outline Dimension | φ25.4 x 44mm |
Physical properties of BBO:
| Crystalline structure | Trigonal, space group R3c, Point group 3m | Cell Parameters | a = b = 12.532 Å, c = 12.717Å, Z = 6 |
| Melting point | 1095±5℃ | Phase transition point | 925±5℃ |
| Optical Homogeneity | δn ~ 10-6 /cm | Mohs hardness | 4 |
| Density | 3.85 g/cm3 | Specific heat | 1.91J/cm3 xK |
| Hydroscopicity | Low | Thermal expansion coefficients | a,4 x 10-6/K;c, 36x 10-6/K |
| Thermal Conductivity | ⊥c,1.2W/m/K; //c, 1.6W/m/K | Absorption Coefficient | < 0.1% /cm (at 1064 nm) |
Optical properties of BBO:
| Transparency Range | 189-3500 nm | Refractive Indices at 1064 nm at 800 nm at 532 nm at 400 nm at 266 nm | no = 1.6545, ne = 1.5392 no = 1.6606, ne = 1.5444 no = 1.6742, ne = 1.5547 no = 1.6930, ne = 1.5679 no = 1.7585, ne = 1.6126 |
| Thermo-optic Coefficients | dno/dT = -9.3 x 10-6 /°C dne/dT = -16.6 x 10-6 /°C | Electro-optic Coefficients | γ11 = 2.7 pm/V, γ22, γ31 < 0.1 γ11 |
| Effective Nonlinearity Expressions | dooe= d31 sinθ +(d11 cos3φ - d22 sin3φ) cosθ deoe= (d11 sin3φ + d22 cos3φ) cos2θ | Half-wave Voltage | 48 kV (at 1064 nm) |
| NLO Coefficients | d11 = 5.8 x d36(KDP) d31 = 0.05 x d11 d22 < 0.05 x d11 | Damage Threshold (Bulk) at 1064 nm at 532 nm | 5 GW/cm2 (10 ns); 10 GW/cm2 (1.3 ns) 1 GW/cm2 (10 ns); 7 GW/cm2 (250 ps) |
| Phase-matchable SH Wavelengths: | 189 - 1750 nm |
Beta BBO Pockels Cells or beta barium borate pockels cells exhibit significant advantages over other materials in terms of laser power handling abilities, temperature endurance, and substantial freedom from piezoelectric ringing. Beta BBO Pockels cells are the most attractive candidates for high repetition rate Q-switching, pulse picking at up to 3 MHz, laser cavity dumping, regenerative amplifier control, and beam chopper. BBO pockels cells are a better option than KDP pockels cells in the field of high repetition rate and high power applications. On account of the low piezoelectric coupling coefficients of the top-notch-quality BBO crystals that we incorporate into our Pockels Cells, our BBO Pockels cells are capable of generating pulses with repetition rates of hundreds of kilohertz.
Shanghai North Optics offers off-the-shelf and custom BBO Pockels Cells with high damage threshold, low insertion loss, high extinction ratio, minimal piezoelectric ringing, and competitive price. BBO Pockels Cells with both Single and double BBO crystal designs and low-voltage geometries are available upon request. Besides, we also offer BBO crystals for EO applications.
To check the stock list of BBO Pockels Cells, please click here.
Click Here to visit our archives to learn more about pockels cells.
Features:
Because it relies on the electro-optical effect, switching time - aided by the low capacitance of the Electro-Optical Q Switch is fast, therefore it has surpassing performance for high repetition rate lasers up to 1MHz. All-solid-state short-cavity Q-switched laser using BBO electro-optic Q-switch can generate high-energy laser with a pulse width of less than 4ns.
Without water cooling, the BBO electro-optical Q switch can be turned off and withstand up to 150W intracavity oscillation optical power (laser output power up to 50W).
BBO crystals have a wide transmission range of 189nm to 3500nm, which allows them to be used in diverse applications from UV to NIR spectrum.
Compared to LiNbo3, BBO crystals are much less impaired by piezoelectric when voltage is applied. The other important feature of BBO electro-optics is their low absorption and associated laser-induced thermal birefringence. Due to the low absorption, very little optical heating will occur at operating wavelengths in the visible and near IR.
BBO has a relatively small electro-optic coefficient, and hence a high operation voltage.
Cautions:
Features of BBO crystal:
Applications:
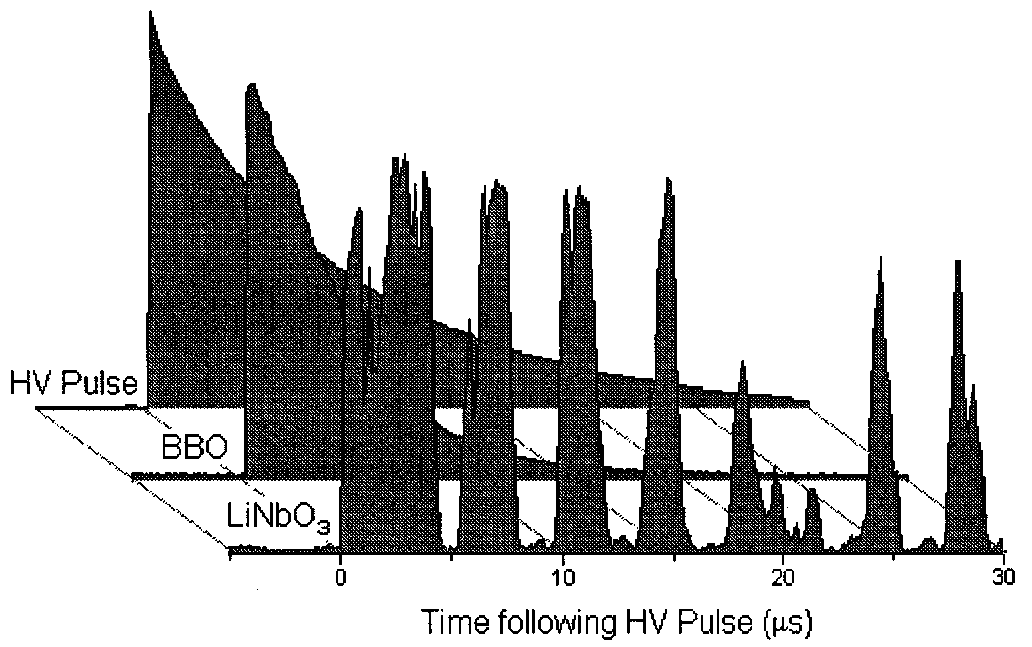
Fig.1 Qualitative comparison of acoustic ringing in BBO and LiNbO3
The intensity transmitted through the LiNbO3 Pockels cell varies greatly due to piezoelectric effects, whereas the light transmitted through the
BBO Pockels cell follows the decay of the applied high voltage pulse with no evident acoustic ringing
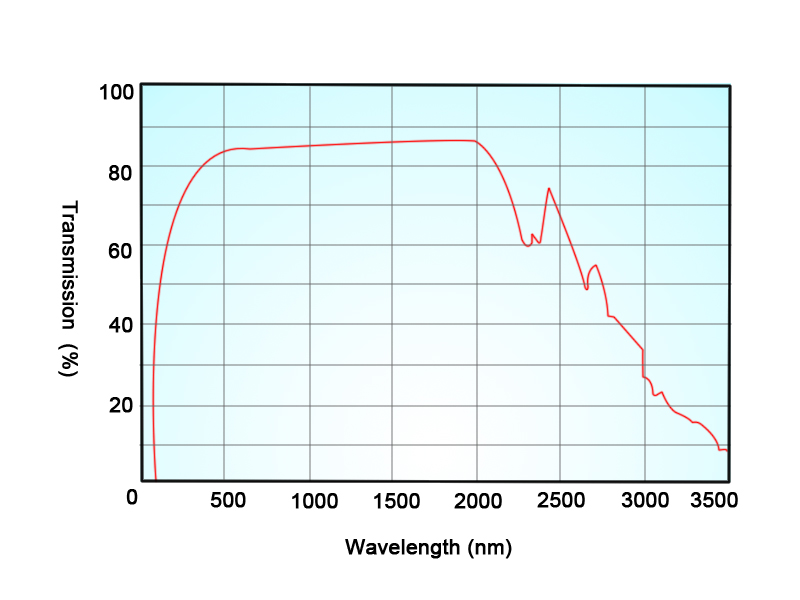
Fig.2 Transparency Curve of BBO crystal
Application Notes:
When it comes to practical applications of Pockels cells, one might need to take some additional side effects into account:
Calculation of Quarter-wave Voltage
The voltage required to produce a retardance of π radians is called the halfwave voltage or simply Vπ. For an optical input linearly polarized 45o applying a halfwave voltage rotates the polarization by 90o. When the output wave is passed through a linear the resultant can be rapidly modulated from maximum intensity to minimum intensity by rapidly changing the voltage applied to the crystal from 0 volts to Vπ.
The halfwave voltage of BBO is dependent on the optical wavelength and is given by:
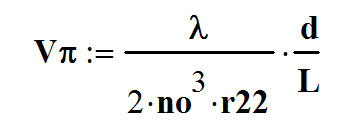
Where λ=optical wavelength
d=electrode spacing
L=optical path length
r22=electro-optic coefficients
no=ordinary indices of refraction
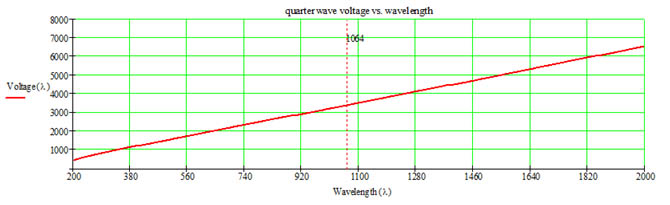
EO Q-Switch 1/4Wave Voltage Vs wavelength (3x3x20mm)
1/4 Wave Voltage @1030nm : Vπ/2 =3388V
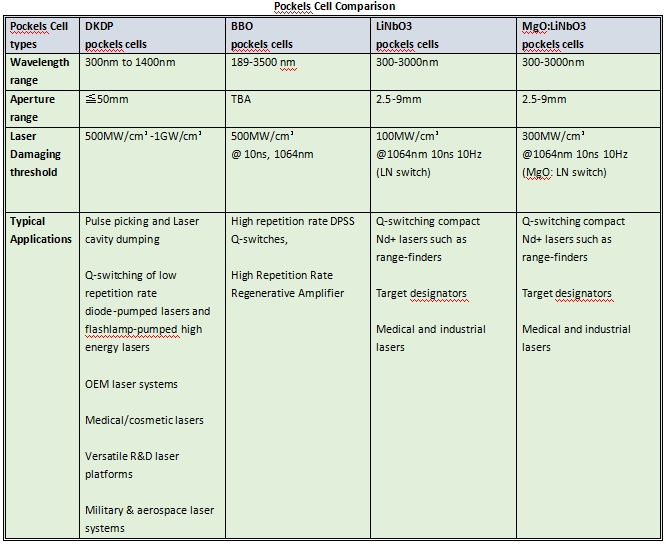
Pockels Cell Comparison Chart: